Yao Group @ HKU Physics
| back | ||
|---|---|---|
Optical control of localized spins in semicondutors for quantum information processing |
||
The important tool is the spatial-temporal engineering of the electromagnetic environment, i.e. the passive control by cavity quantum electrodynamics and the active control by shaped laser pulses. In collaboration with L. J. Sham and Renbao Liu, we developed theories for control of spin and photon dynamics in the integrated semiconductor structures composed of quantum dots, microcavities and waveguides. These control schemes can enable the following essential components for scalable distributed quantum computation: (a) quantum network functions for transferring, swapping, and deterministically entangling spin qubits at distant quantum nodes (see our papers [2] & [4]); (b) ultra-fast initialization and quantum nondemolition measurement of the spin qubit in quantum dot (see [3]); (c) phase gate and entanglement operation for photon qubits in optical waveguide (see [1]). |
||
|
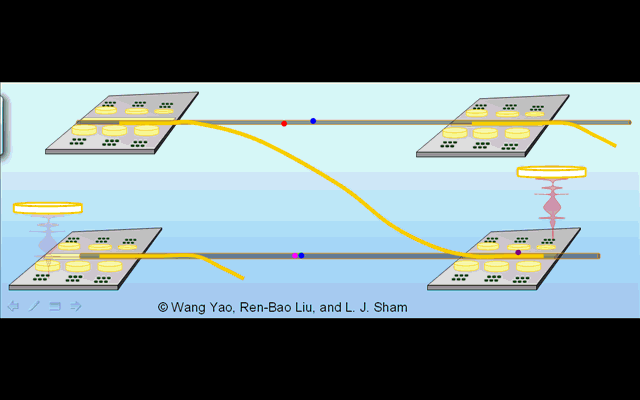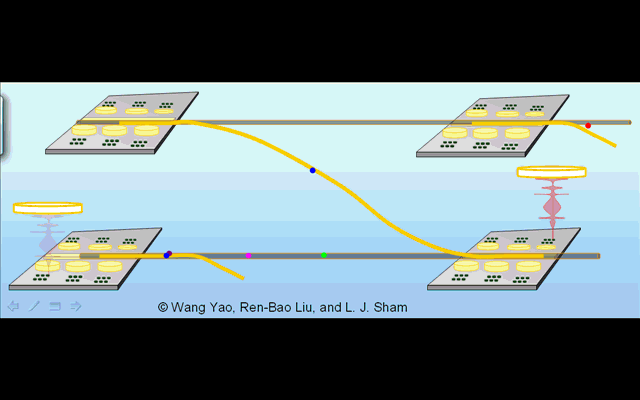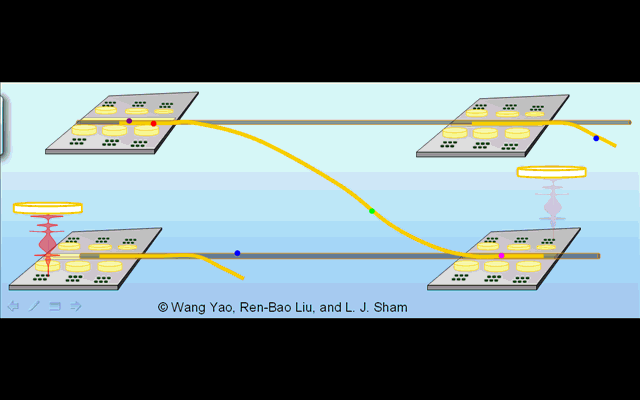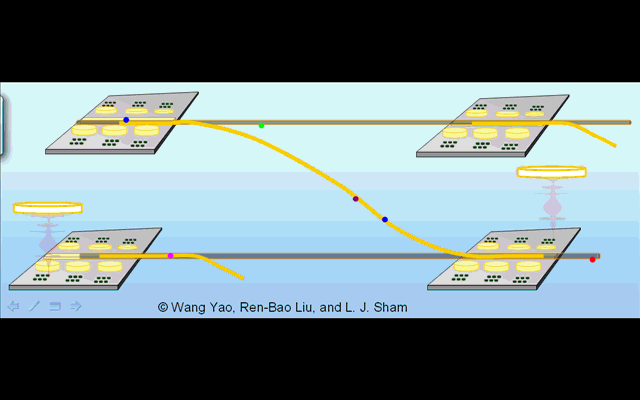
Illustration 1. Distributed architechture for optically controlled solid-state quantum computer. |
|
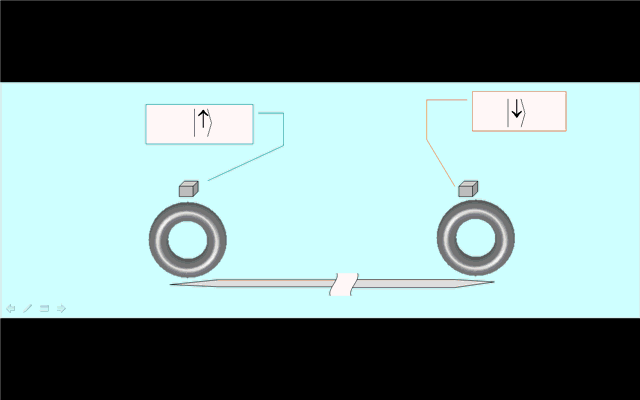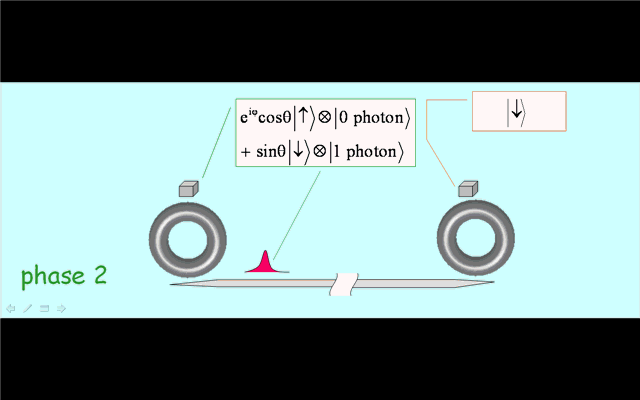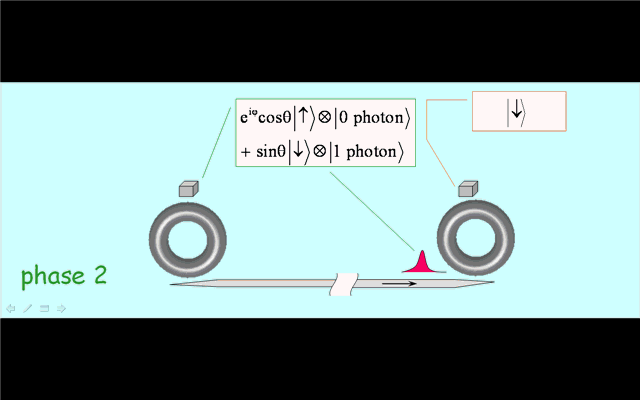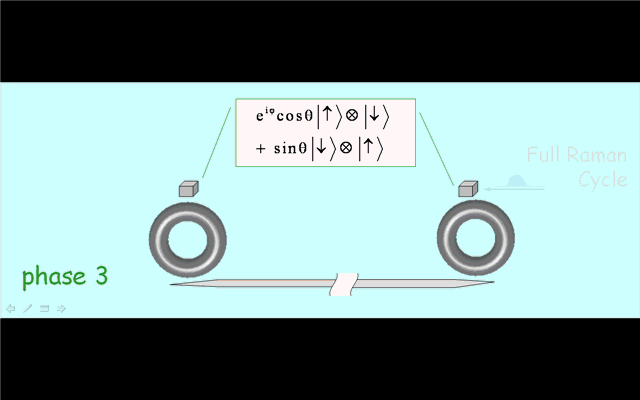
Illustration 2. Deterministic creation of nonlocal entanglement in the quantum network. Operation phase 1: generation of spin-photon entanglement by a partial cycle of cavity assisted Raman process at the sending node. Phase 2: photon propagation in the quantum channel. Phase 3: trapping of the photon into the receiving node by a full Raman cycle. |
||